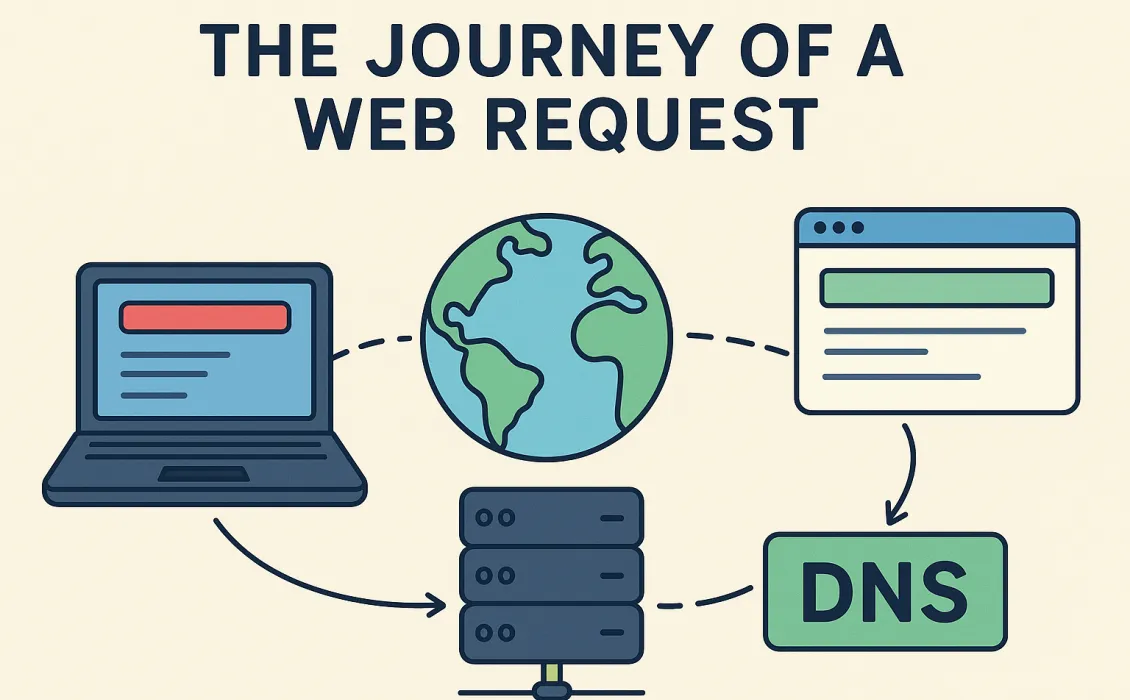
When we type a URL into a browser, such as https://raheelshan.com, we rarely think about what happens next. Behind that simple action, there is a layered process involving domains, hosting, servers, network protocols, and several checks before we ever reach a file like index.php.
Most people assume a domain is simply a website's title, but in reality, it represents an entire industry built around digital identity, ownership, and business opportunity. Think of it as digital real estate.
The Domain Layer
The journey begins when we type an address such as:
https://raheelshan.com
A domain is a human-friendly identifier. Computers don’t communicate using names; they communicate using IP addresses. Domains exist so humans have something simpler to remember.
Before anything else occurs, the browser needs to determine whether this domain exists and who manages it.
What Is a Domain Name?
A domain name is a human-friendly address used to reach a website. Computers communicate using IP addresses such as 178.128.23.91. Domains exist so humans can remember names instead of numbers.
A domain does not point to a server automatically. Ownership and configuration are required before it becomes usable.
The Domain Ecosystem
The domain world operates under three main components:
Registry: The global operator of domain extensions that maintains the master database.
Registrar: Domain registration companies like Godaddy, Domain.com, Namecheap, etc.
Registrant: A person or company who buys the domain and owns the right to use the domain.
Why Do Domains Expire?
Domains are not purchased permanently. They are leased. The registrant pays for the right to use the name for a limited period (1–5 years). When the lease expires:
- The registrar disables the domain.
- It enters a grace period.
- After a final redemption phase, it is released publicly.
This expiration cycle is what powers the domain investing industry.
Country-Level Domains (ccTLDs)
Not every domain ends in .com or .net. Many domains are tied to countries.
| Domain Type | Examples | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Country Code TLDs (ccTLD) |
.ca, .pk, .uk, .in, .jp
|
Represent a specific country |
| Registry Example |
.pk is managed by PKNIC
|
|
| Restrictions | Some require proof of citizenship or business presence |
Specialized domain categories exist:
.govis reserved for government entities.eduis restricted to educational institutions
New & Custom Domain Extensions (gTLDs)
Beyond .com, the internet now supports hundreds of modern domain extensions such as:
.dev.app.store.io.ai
These are released and managed by ICANN-approved registry operators. They provide branding flexibility, especially for startups.
Examples:
| Extension | Popular Usage |
|---|---|
.dev
|
Developers and tech sites |
.io
|
SaaS and startup products |
.ai
|
AI and machine-learning platforms |
The Domain Industry: Buying, Selling, and Trading Domains
Domains behave like digital real estate. A large business ecosystem exists around them, and they do lots of things. Let me mention a few.
- Domain Investing: But valuable domains to sell later on at higher prices.
- Domain Tracking: Tracking domains that will expire soon and attempting to acquire them to sell at their own demanded price.
- Domain Auctions: Competitive bidding on high-demand domains.
- Domain Brokering: Professionals negotiate deals on already-owned domains.
Some domains are sold for thousands or even millions purely because of branding potential.
DNS Comes Next
The domain layer concludes once:
- the domain exists,
- is owned by someone,
- and has assigned nameservers.
Only then can the browser attempt to locate the hosting server.
That leads to Part 2 of this series:
The Journey of a Web Request – Part 2: DNS and Nameservers
Conclusion
Domains are the identity layer of the internet. They represent ownership, branding, business value, and technical configuration. Understanding domains helps us appreciate how something as simple as typing a URL triggers an entire global ecosystem before a single request ever reaches a server.